The damage characteristics and spatial distribution pattern of the new maize pest Paralipsa gularis (Zeller) in southwestern China
中文摘要:【目的】 明确中国西南地区新发玉米害虫一点缀螟
Paralipsa gularis (Zeller) 幼虫对玉米的为害特征和空间分布,为田间预测预报与防治工作提供理论支撑。
【方法】 采用5点随机取样法对云南省江城县玉米田一点缀螟幼虫的发生与为害情况进行抽样调查,通过聚集度指标法和回归分析法分析幼虫在玉米田的空间分布。
【结果】 田间调查发现,幼虫自玉米乳熟期开始为害,通过钻蛀玉米果穗、穗芯及茎秆,造成籽粒残缺,并引发穗腐。为害部位有明显的蛀孔和钻蛀隧道,并产生的白色排泄物,老熟幼虫在玉米苞叶和果穗上吐丝结茧化蛹。幼虫平均密度范围为0.02-3.62头/株,玉米受害株率为2%-58%,玉米果穗受害率与虫口密度呈正相关。幼虫在玉米果穗上呈聚集分布,个体间相互吸引,分布的基本成分为个体群。聚集均数
l分析表明,幼虫聚集的原因是由环境因素所导致的。基于空间分布型的研究结果,建立了一点缀螟幼虫的理论抽样公式
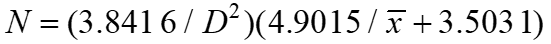
和基于幼虫密度防治指标的最佳序贯抽样公式
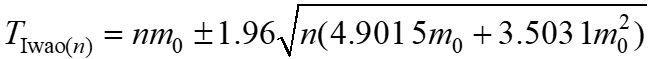
。
【结论】 本文明确了玉米田一点缀螟的为害特征及其空间分布,提出了田间种群的抽样方法,为田间幼虫种群密度的调查和防治工作提供了技术支撑。
英文摘要:[Objectives] To clarify the damage characteristics and spatial distribution of larvae
of
Paralipsa gularis (Zeller), an emerging pest of maize in southwestern
China, in order to provide theoretical support for the prediction and control
of this species.
[Methods] A
five-point random sampling method was used to survey the occurrence and damage
caused by
P. gularis larvae in summer maize fields in Jiangcheng county,
Yunnan province. The spatial distribution patterns of larvae in maize fields
were analyzed using the aggregation index method and regression analysis.
[Results] Field investigations found that larvae
began to damage maize during the milk stage, and bored into maize ears, cores
and stalks, causing grain defects and ear rot. Damaged areas had obvious borer
holes, tunnels and white excrement, and mature larvae pupated on maize bracts
and ears. Average larval densities ranged from 0.02 to 3.62 individuals per
plant, and the rate of maize-damaged plants was 2% to 58%. The rate of damage
to maize ears was positively correlated with average larval density. Larvae had
an aggregated distribution in maize ears, indicating that individuals attracted
each other. The basic component of the distribution was the individual group.
The aggregation average
l indicated that larvae aggregated in response to
environmental factors. Based on these results, we derived the theoretical sampling formula:
 ,
, for larvae of
P. gularis and the larval density control index sampling formula:
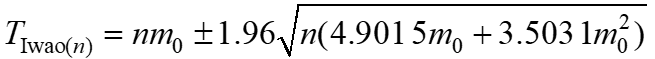
.
[Conclusion] The damage characteristics, spatial distribution habits of
P. gularis larvae in maize fields were determined and a sampling method for field
populations proposed. The results provide a scientific basis for population
density surveys and the control of
this pest
in maize fields.